
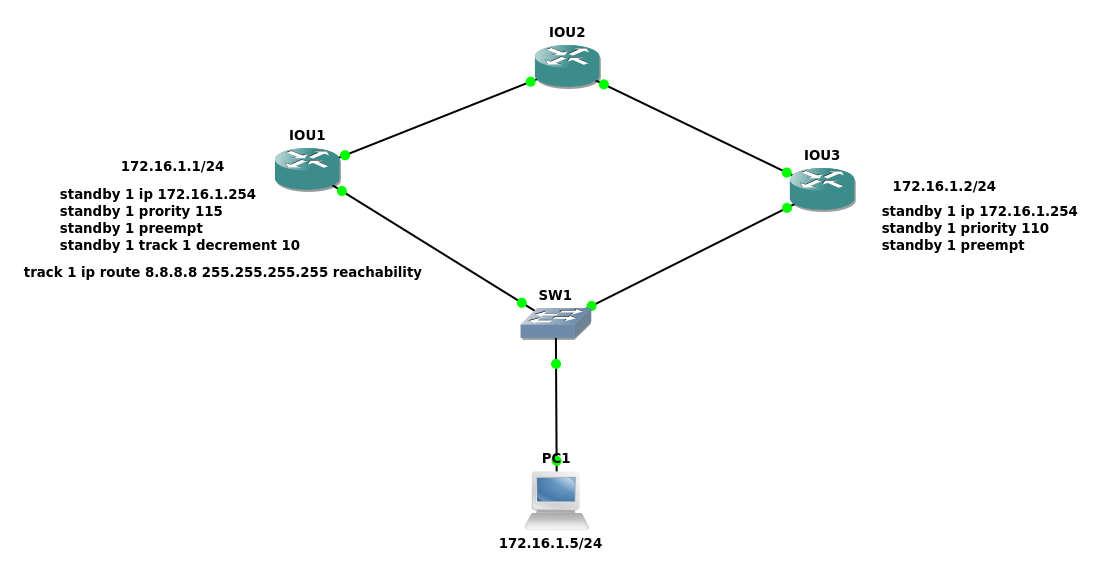
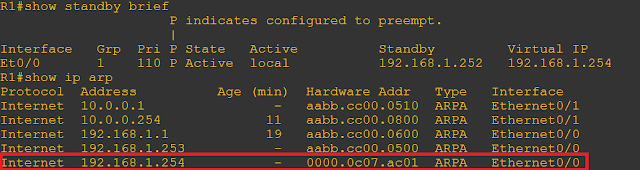
Where XX is VRID - VRRP Virtual Router Identifier up to 255 IDs. Uses the multicast address of 224.0.0.18 and a protocol number of 112.Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol– VRRP: Default priority is 100 (highest is better), when equal highest IP address wins.Group number range is 0 to 4095 for easier mapping with VLAN IDs for extended range.Version 1 defines a multicast address of 224.0.0.2 is used to send HSRP hello messages but was later rectified in version 2 with 224.0.0.102.Each of them has their pros and cons depending on the requirements. First Hop Redundancy Protocols are majorly divided into three, HSRP, VRRP and GLBP, are to protect failure in the data plane when the default gateway fails by defining a default gateway where the routers agree on.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
